Списъците са една от най-използваните структури от данни в Python. Ние продължаваме да използваме списъци в много различни приложения, от решаване на прости проблеми до сложни проблеми. В Python списъците заместват масиви с предимства като:
- Динамични по размер
- Може да съхранява елементи от различни типове данни в един списък
Можем да имаме достъп до данните просто от списъци, както са подредени; за разлика от наборите, данните ще бъдат неподредени. За достъп до данните можем да използваме няколко начина за итерация през всеки елемент в списъка. Този урок обхваща всички начини с примери.
1. Примки
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] count = 0 while (count <len(list1)): 1 print (list1 [count]) count="count" + < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We created a list with a few elements. Initially, count = 0. We're printing the element at the 'count' index and incrementing the count in the while loop. When the count reaches the length of the list, the loop will be terminated, and all the elements will already be accessed.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>count = 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> <tr> <td>count = 5 = len (list1)</td> <td>-</td> <td>-</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <tr><td>Using for loop:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i in list1: print (i) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-2.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>Using for-in, we accessed all the i's, the elements inside the list.</p> <ul> <tr><td>Using for and range:</td> </tr></ul> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i]) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-3.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The range function helps the 'for' loop to iterate from 0 to the given list's length.</p> <p> <strong>Mechanism:</strong> </p> <table class="table"> <tr> <td>the range gives - 0</td> <td>list1 [0]</td> <td>3</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 1</td> <td>list1 [1]</td> <td>5</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 2</td> <td>list1 [2]</td> <td>7</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 3</td> <td>list1 [3]</td> <td>2</td> </tr> <tr> <td>the range gives - 4</td> <td>list1 [4]</td> <td>4</td> </tr> </table> <ul> <li>The range function doesn't give the last element specified - len (list1) = 5 is not given.</li> </ul> <h2>2. Using List Comprehension</h2> <p>This is the simple and suggested way to iterate through a list in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ') </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-4.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We can use for loops inside a list comprehension. We used the same for loops we used in the above examples but inside a list in a single line. This way, we can reduce the length of the code and also list comprehension is a very subtle and efficient way to put loops in lists.</p> <h2>3. Using enumerate():</h2> <p>The enumerate function converts the given list into a list of tuples. Another important fact about this function is that it keeps count of the iterations. This is a built-in function in Python.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-5.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <h2>4. Using lambda function and map():</h2> <p>These are anonymous functions. There is a function map () in Python that can accept a function as an argument, and it calls the function with every element in the iterable, and a new list with all the elements from the iterable will be returned.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-6.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>The lambda num: num is given as an input to the map function along with the list. The function will take every single element in the list, accept it, and then return it. The map () function will pass the list elements one by one to the lambda function to return the elements.</p> <h2>What if we want to Iterate Multi-dimensional Lists?</h2> <p>There is an inbuilt module in Python designed to perform operations on multi-dimensional lists.</p> <p> <strong>1. To get numpy:</strong> </p> <p>Check if Python and pip are installed by opening the cmd via search and typing the commands:</p> <p> <strong>Python -version</strong> </p> <p> <strong>Pip --version</strong> </p> <p>If both Python and PIP are present in our system, it is now time to install our library:</p> <p> <strong>2. Open cmd from the start menu</strong> </p> <p> <strong>3. Type the command</strong> </p> <h3>pip install numpy</h3> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p>All the library packages, data, and sub-packages will be installed one after the other.</p> <p> <strong>Code:</strong> </p> <pre> import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x) </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/python-tutorial/43/how-iterate-through-list-python-7.webp" alt="How to Iterate through a List in Python"> <p> <strong>Understanding:</strong> </p> <p>We imported the numpy module. Using the arrange method, we created an array with 9 elements. We accessed the list by reshaping it to 3 * 3 (rows * columns) using the reshape. Using the nditer function, we printed each element in the list.</p> <hr></len(list1)):>
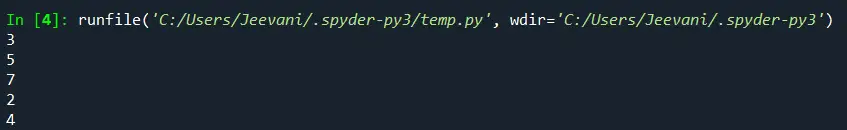
Изход:

разбиране:
Използвайки for-in, ние получихме достъп до всички i-та, елементите в списъка.
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] length = len (list1) for i in range (0, len (list1)): print (list1 [i])
Изход:

разбиране:
Функцията за диапазон помага на цикъла 'for' да итерира от 0 до дължината на дадения списък.
java докато условие
Механизъм:
| диапазонът дава - 0 | лист1 [0] | 3 |
| диапазонът дава - 1 | лист1 [1] | 5 |
| диапазонът дава - 2 | лист1 [2] | 7 |
| диапазонът дава - 3 | лист1 [3] | 2 |
| диапазонът дава - 4 | лист1 [4] | 4 |
- Функцията за диапазон не дава последния указан елемент - len (списък1) = 5 не е даден.
2. Използване на списък с разбиране
Това е простият и препоръчан начин за итерация през списък в Python.
Код:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] [print (i) for i in list1] print (' ') [print (list1 [i]) for i in range (0, len (list1))] print (' ')
Изход:

разбиране:
какво е структура в структурата на данните
Можем да използваме for цикли вътре в разбиране на списък. Използвахме същите цикли for, които използвахме в горните примери, но вътре в списък в един ред. По този начин можем да намалим дължината на кода, а също така разбирането на списъци е много фин и ефективен начин за поставяне на цикли в списъци.
3. Използване на enumerate():
Функцията enumerate преобразува дадения списък в списък от кортежи. Друг важен факт за тази функция е, че тя поддържа броя на повторенията. Това е вградена функция в Python.
Код:
list1 = [3, 5, 7, 2, 4] for i, j in enumerate (list1): print ('index = ', i, 'value: ', j)
Изход:

4. Използване на ламбда функция и map():
Това са анонимни функции. Има функция map () в Python, която може да приеме функция като аргумент и извиква функцията с всеки елемент в итерируемия елемент и ще бъде върнат нов списък с всички елементи от итерируемия.
Код:
list1 = [3, 6, 1, 8, 7] result = list (map (lambda num: num, list1)) print (result)
Изход:

разбиране:
Ламбда num: num се дава като вход към функцията map заедно със списъка. Функцията ще вземе всеки отделен елемент в списъка, ще го приеме и след това ще го върне. Функцията map () ще предаде елементите на списъка един по един на ламбда функцията, за да върне елементите.
Ами ако искаме да итерираме многомерни списъци?
В Python има вграден модул, предназначен да извършва операции върху многоизмерни списъци.
1. За да получите numpy:
Проверете дали Python и pip са инсталирани, като отворите cmd чрез търсене и въведете командите:
Python -версия
Pip --версия
Ако както Python, така и PIP присъстват в нашата система, сега е време да инсталираме нашата библиотека:
java списък
2. Отворете cmd от стартовото меню
3. Въведете командата
pip инсталирайте numpy
Всички библиотечни пакети, данни и подпакети ще бъдат инсталирани един след друг.
Код:
import numpy list1 = numpy. arange (9) list1 = list1. reshape (3, 3) for x in numpy. nditer (list1): print (x)
Изход:
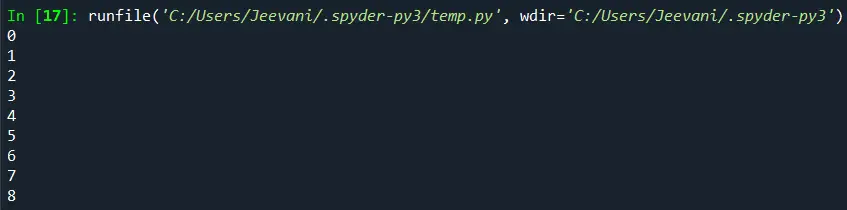
разбиране:
Импортирахме модула numpy. Използвайки метода arrange, създадохме масив с 9 елемента. Осъществихме достъп до списъка, като го преоформихме до 3 * 3 (редове * колони), използвайки преоформянето. С помощта на функцията nditer отпечатахме всеки елемент в списъка.
