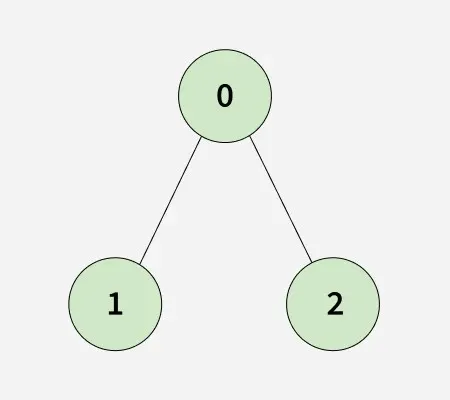
Като се има предвид a свързан неориентиран граф представен от списък на съседство adjList[][] с п възли и м ръбове, като всеки възел има a различен етикет от 0 до n-1 и всеки adj[i] представлява списък от върхове, свързани с връх i.
Създайте a клонинг на графиката, където всеки възел в графиката съдържа цяло число вал и масив ( съседи ) от възли съдържащи възли, които са съседни на текущия възел.
клас възел {
val: цяло число
съседи: списък [възел]
}
Вашата задача е да клонирате дадената графика и да върнете препратка към клонираната графика.
Забележка: Ако върнете правилно копие на дадената графика, резултатът ще бъде верен; в противен случай, ако копието е неправилно, ще се отпечата невярно.
Примери
вход: n = 4 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0 2] [0 1 3] [2]]
Изход: вярно
Обяснение:
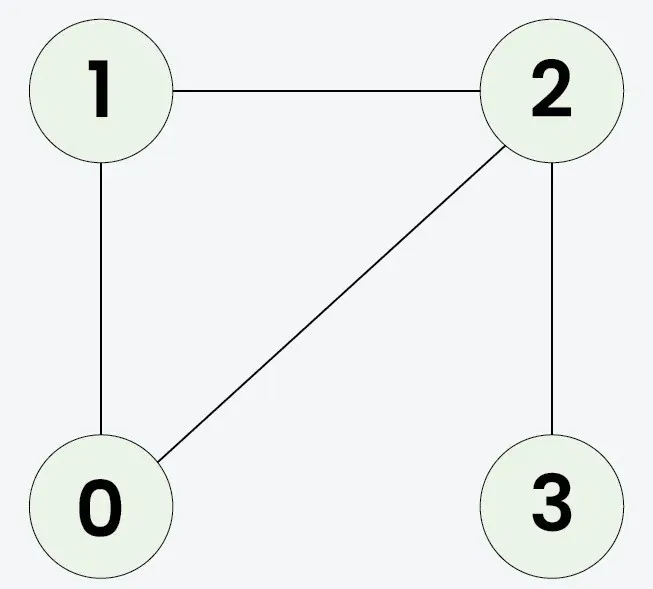
Тъй като клонираната графика е идентична с оригинала, резултатът ще бъде верен.вход: n = 3 adjList[][] = [[1 2] [0] [0]]
Изход: вярно
Обяснение:
Тъй като клонираната графика е идентична с оригинала, резултатът ще бъде верен.
примери за операционна система
Съдържание
- Защо трябва да проследяваме посетените/клонирани възли?
- Как да следите посетените/клонирани възли?
- Как да свържете клонирани възли?
- Как да проверя дали клонираната графика е правилна?
- [Подход 1] Използване на BFS преминаване - O(V+E) време и O(V) пространство
- [Подход 2] Използване на DFS обхождане - O(V+E) време и O(V) пространство
Защо трябва да проследяваме посетените/клонирани възли?
Трябва да проследяваме посетени или клонирани възли, за да избегнем безкрайна рекурсия и излишна работа при клониране на графика. Тъй като графиките могат да съдържат цикли (където възел може да сочи обратно към предишно посетен възел), без да следим възлите, които вече сме клонирали, функцията за клониране безкрайно ще преразглежда същите възли, което води до препълване на стека или неправилно дублиране.
Как да следите посетените/клонирани възли?
HashMap/Map е необходим, за да се поддържат всички възли, които вече са създадени. Магазини за ключове : Референция/адрес на оригиналния възел Магазини за стойност : Референция/адрес на клониран възел Направено е копие на всички възли на графиката.
Как да свържете клонирани възли?
При посещение на съседните върхове на a възел в вземете съответното клониране възел за вас да наречем това IN сега посетете всички съседни възли за в и за всеки съсед намерете съответния клониран възел (ако не бъде намерен, създайте такъв) и след това натиснете в съседния вектор на IN възел.
Как да проверя дали клонираната графика е правилна?
Извършете BFS обхождане на оригиналната графика преди клониране и след това отново на клонираната графика, след като клонирането приключи. По време на всяко обхождане отпечатайте стойността на всеки възел заедно с неговия адрес (или препратка). За да проверите правилността на клонирането, сравнете реда на възлите, посетени в двете обхождания. Ако стойностите на възлите се появяват в същия ред, но техните адреси (или препратки) се различават, това потвърждава, че графиката е била успешно и правилно клонирана.
Разгледайте как да клониране на неориентиран граф, включително графики с множество свързани компоненти използване на BFS или DFS, за да се осигури пълно дълбоко копие на всички възли и ръбове.
[Подход 1] Използване на BFS преминаване - O(V+E) време и O(V) пространство
C++При подхода BFS графиката се клонира итеративно с помощта на опашка. Започваме с клониране на първоначалния възел и поставянето му в опашката. Докато обработваме всеки възел от опашката, ние посещаваме неговите съседи. Ако съсед все още не е клониран, ние създаваме клонинг, който го съхранява в карта и го поставя в опашка за по-късна обработка. След това добавяме клонинга на съседа към списъка със съседи на клонинга на текущия възел. Този процес продължава ниво по ниво, като гарантира, че всички възли са посетени в ред на ширина на първо място. BFS е особено полезен за избягване на дълбока рекурсия и ефективно боравене с големи или широки графики.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { public int val; public ArrayList<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; Map<Node Node> mp = new HashMap<>(); Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>(); // Clone the starting node Node clone = new Node(node.val); mp.put(node clone); q.offer(node); while (!q.isEmpty()) { Node current = q.poll(); for (Node neighbor : current.neighbors) { // Clone neighbor if it hasn't been cloned yet if (!mp.containsKey(neighbor)) { mp.put(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.offer(neighbor); } // Add the clone of the neighbor to the current node's clone mp.get(current).neighbors.add(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node2 node3))); node2.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node3))); node3.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node1 node2 node4))); node4.neighbors.addAll(new ArrayList<> (Arrays.asList(node3))); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static boolean compareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || n1 == n2) return false; visited.put(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.size() != n2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node neighbor1 = n1.neighbors.get(i); Node neighbor2 = n2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) != neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); boolean isEqual = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
from collections import deque # Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0): self.val = val self.neighbors = [] # Clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): if not node: return None # Map to hold original nodes as keys and their clones as values mp = {} # Initialize BFS queue q = deque([node]) # Clone the starting node mp[node] = Node(node.val) while q: current = q.popleft() for neighbor in current.neighbors: # If neighbor not cloned yet if neighbor not in mp: mp[neighbor] = Node(neighbor.val) q.append(neighbor) # Link clone of neighbor to the clone of the current node mp[current].neighbors.append(mp[neighbor]) return mp[node] # Build graph def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs structurally and by values def compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): if not n1 or not n2: return n1 == n2 if n1.val != n2.val or n1 is n2: return False visited[n1] = n2 if len(n1.neighbors) != len(n2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(n1.neighbors)): neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i] neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i] if neighbor1 in visited: if visited[neighbor1] != neighbor2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited): return False return True # Driver if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() cloned = cloneGraph(original) result = compareGraphs(original cloned {}) print('true' if result else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // Definition for a Node public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Clone the graph public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { if (node == null) return null; var mp = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); var q = new Queue<Node>(); // Clone the starting node var clone = new Node(node.val); mp[node] = clone; q.Enqueue(node); while (q.Count > 0) { var current = q.Dequeue(); foreach (var neighbor in current.neighbors) { // If neighbor not cloned clone it and enqueue if (!mp.ContainsKey(neighbor)) { mp[neighbor] = new Node(neighbor.val); q.Enqueue(neighbor); } // Add clone of neighbor to clone of current mp[current].neighbors.Add(mp[neighbor]); } } return mp[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { var node1 = new Node(0); var node2 = new Node(1); var node3 = new Node(2); var node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node2 node3 }); node2.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node3 }); node3.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node1 node2 node4 }); node4.neighbors.AddRange(new[] { node3 }); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structure and value public static bool CompareGraphs(Node n1 Node n2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (n1 == null || n2 == null) return n1 == n2; if (n1.val != n2.val || ReferenceEquals(n1 n2)) return false; visited[n1] = n2; if (n1.neighbors.Count != n2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.Count; i++) { var neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; var neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(neighbor1)) { if (!ReferenceEquals(visited[neighbor1] neighbor2)) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } public static void Main() { var original = BuildGraph(); var cloned = CloneGraph(original); var visited = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); Console.WriteLine(CompareGraphs(original cloned visited) ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Clone the graph function cloneGraph(node) { if (!node) return null; const mp = new Map(); const q = [node]; // Clone the initial node mp.set(node new Node(node.val)); while (q.length > 0) { const current = q.shift(); for (const neighbor of current.neighbors) { if (!mp.has(neighbor)) { mp.set(neighbor new Node(neighbor.val)); q.push(neighbor); } // Link clone of neighbor to clone of current mp.get(current).neighbors.push(mp.get(neighbor)); } } return mp.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors = [node2 node3]; node2.neighbors = [node1 node3]; node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4]; node4.neighbors = [node3]; return node1; } // Compare two graphs structurally and by value function compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited = new Map()) { if (!n1 || !n2) return n1 === n2; if (n1.val !== n2.val || n1 === n2) return false; visited.set(n1 n2); if (n1.neighbors.length !== n2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < n1.neighbors.length; i++) { const neighbor1 = n1.neighbors[i]; const neighbor2 = n2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(neighbor1)) { if (visited.get(neighbor1) !== neighbor2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(neighbor1 neighbor2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver const original = buildGraph(); const cloned = cloneGraph(original); const result = compareGraphs(original cloned); console.log(result ? 'true' : 'false');
Изход
true
[Подход 2] Използване на DFS обхождане - O(V+E) време и O(V) пространство
C++При подхода DFS графиката се клонира с помощта на рекурсия. Започваме от дадения възел и изследваме, доколкото е възможно, всеки клон, преди да се върнем назад. Карта (или речник) се използва за проследяване на вече клонирани възли, за да се избегне обработката на един и същ възел многократно и за обработка на цикли. Когато срещнем възел за първи път, създаваме негов клонинг и го съхраняваме в картата. След това за всеки съсед на този възел рекурсивно го клонираме и добавяме клонирания съсед към клонинга на текущия възел. Това гарантира, че всички възли са посетени задълбочено преди връщане и структурата на графиката е вярно копирана.
#include
import java.util.*; // Definition for a Node class Node { int val; ArrayList<Node> neighbors; Node() { neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } Node(int val) { this.val = val; neighbors = new ArrayList<>(); } } public class GfG { // Map to hold original node to its copy static HashMap<Node Node> copies = new HashMap<>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node cloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.containsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies.put(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (Node neighbor : node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.add(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph public static Node buildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node2 node3)); node2.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1 node3)); node3.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node1node2 node4)); node4.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node3)); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static boolean compareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 HashMap<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited.put(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.size() != node2.neighbors.size()) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.size(); i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors.get(i); Node n2 = node2.neighbors.get(i); if (visited.containsKey(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) != n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { Node original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph Node cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph boolean result = compareGraphs(original cloned new HashMap<>()); System.out.println(result ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
# Definition for a Node class Node: def __init__(self val=0 neighbors=None): self.val = val self.neighbors = neighbors if neighbors is not None else [] # Map to hold original node to its copy copies = {} # Function to clone the graph def cloneGraph(node): # If the node is None return None if not node: return None # If node is not yet cloned clone it if node not in copies: # Create a clone of the node clone = Node(node.val) copies[node] = clone # Recursively clone neighbors for neighbor in node.neighbors: clone.neighbors.append(cloneGraph(neighbor)) # Return the clone return copies[node] def buildGraph(): node1 = Node(0) node2 = Node(1) node3 = Node(2) node4 = Node(3) node1.neighbors = [node2 node3] node2.neighbors = [node1 node3] node3.neighbors = [node1 node2 node4] node4.neighbors = [node3] return node1 # Compare two graphs for structural and value equality def compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited): if not node1 or not node2: return node1 == node2 if node1.val != node2.val or node1 is node2: return False visited[node1] = node2 if len(node1.neighbors) != len(node2.neighbors): return False for i in range(len(node1.neighbors)): n1 = node1.neighbors[i] n2 = node2.neighbors[i] if n1 in visited: if visited[n1] != n2: return False else: if not compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited): return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': original = buildGraph() # Clone the graph using DFS cloned = cloneGraph(original) # Compare original and cloned graph visited = {} print('true' if compareGraphs(original cloned visited) else 'false')
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int val; public List<Node> neighbors; public Node() { val = 0; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } public Node(int _val) { val = _val; neighbors = new List<Node>(); } } class GfG { // Dictionary to hold original node to its copy static Dictionary<Node Node> copies = new Dictionary<Node Node>(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS public static Node CloneGraph(Node node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node == null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.ContainsKey(node)) { Node clone = new Node(node.val); copies[node] = clone; // Recursively clone neighbors foreach (Node neighbor in node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.Add(CloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies[node]; } // Build graph public static Node BuildGraph() { Node node1 = new Node(0); Node node2 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.Add(node2); node1.neighbors.Add(node3); node2.neighbors.Add(node1); node2.neighbors.Add(node3); node3.neighbors.Add(node1); node3.neighbors.Add(node2); node3.neighbors.Add(node4); node4.neighbors.Add(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality public static bool CompareGraphs(Node node1 Node node2 Dictionary<Node Node> visited) { if (node1 == null || node2 == null) return node1 == node2; if (node1.val != node2.val || node1 == node2) return false; visited[node1] = node2; if (node1.neighbors.Count != node2.neighbors.Count) return false; for (int i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.Count; i++) { Node n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; Node n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.ContainsKey(n1)) { if (visited[n1] != n2) return false; } else { if (!CompareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { Node original = BuildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS Node cloned = CloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph bool isEqual = CompareGraphs(original cloned new Dictionary<Node Node>()); Console.WriteLine(isEqual ? 'true' : 'false'); } }
// Definition for a Node class Node { constructor(val = 0) { this.val = val; this.neighbors = []; } } // Map to hold original node to its copy const copies = new Map(); // Function to clone the graph using DFS function cloneGraph(node) { // If the node is NULL return NULL if (node === null) return null; // If node is not yet cloned clone it if (!copies.has(node)) { const clone = new Node(node.val); copies.set(node clone); // Recursively clone neighbors for (let neighbor of node.neighbors) { clone.neighbors.push(cloneGraph(neighbor)); } } // Return the clone return copies.get(node); } // Build graph function buildGraph() { const node1 = new Node(0); const node2 = new Node(1); const node3 = new Node(2); const node4 = new Node(3); node1.neighbors.push(node2 node3); node2.neighbors.push(node1 node3); node3.neighbors.push(node1 node2 node4); node4.neighbors.push(node3); return node1; } // Compare two graphs for structural and value equality function compareGraphs(node1 node2 visited = new Map()) { if (!node1 || !node2) return node1 === node2; if (node1.val !== node2.val || node1 === node2) return false; visited.set(node1 node2); if (node1.neighbors.length !== node2.neighbors.length) return false; for (let i = 0; i < node1.neighbors.length; i++) { const n1 = node1.neighbors[i]; const n2 = node2.neighbors[i]; if (visited.has(n1)) { if (visited.get(n1) !== n2) return false; } else { if (!compareGraphs(n1 n2 visited)) return false; } } return true; } // Driver Code const original = buildGraph(); // Clone the graph using DFS const cloned = cloneGraph(original); // Compare original and cloned graph console.log(compareGraphs(original cloned) ? 'true' : 'false');
Изход
true