Дадена е правоъгълна хартия с размери a x b . Задачата е да изрежете цялата хартия на минимум брой на квадрат парчета. Можем да изберем квадратни парчета с всякакъв размер, но те трябва да бъдат нарязани без припокриване или оставяне на допълнително пространство .
Примери:
вход: a = 5 b = 8
5 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 5 X 8
Изход: 5
Обяснение: Можем да нарежем хартията на 5 квадрата: 1 квадрат с размер 5x5 1 квадрат с размер 3x3 1 квадрат с размер 2x2 и 2 квадрата с размер 1x1.вход: a = 13 b = 11
6 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 13 X 11
Изход: 6
Обяснение: Можем да нарежем хартията на 6 квадрата: 1 квадрат с размер 7x7 1 квадрат с размер 6x6 1 квадрат с размер 5x5 2 квадрата с размер 4x4 и 1 квадрат с размер 1x1.булево към низ javaвход: a = 6 b = 7
5 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 6 X 7
Изход: 5
Обяснение: Можем да нарежем хартията на 5 квадрата: 1 квадрат с размер 4x4, 2 квадрата с размер 3x3 и 2 квадрата с размер 3x3.баш ако друго
Съдържание
- [Неправилен подход 1] Използване на алчна техника
- [Неправилен подход 2] Използване на динамично програмиране
- [Правилен подход] Използване на DFS и динамично програмиране
[Неправилен подход 1] Използване на алчна техника
На пръв поглед може да изглежда, че проблемът може лесно да се реши, като първо изрежем възможно най-големия квадрат от хартията, последвано от изрязване на най-големия квадрат от останалата хартия и така докато изрежем цялата хартия. Но това решение е неправилно.
Защо Greedy Approach не работи?
Помислете за хартия с размер 6x7 тогава, ако се опитаме да изрежем хартията алчно, ще получим 7 квадрати: 1 квадрат с размер 6x6 и 6 квадрата с размер 1x1 докато правилното решение е: 5. Следователно алчният подход няма да работи.
[Неправилен подход 2] Използване на динамично програмиране
Динамично програмиране с вертикални или хоризонтални срезове: Друго решение, което може да изглежда правилно, е използването Динамично програмиране . Можем да поддържаме таблица dp[][] така, че dp[i][j] = минимален брой квадрати, които могат да бъдат изрязани от хартия с размер i x j . След това за хартия с размер axb
- Можем да опитаме да го разрежем по всеки ред: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i - k][j] + dp[k][j]) където k може да бъде в диапазона [1 i - 1].
- Можем да опитаме да го изрежем по всяка колона: dp[i][j] = min(dp[i][j] 1 + dp[i][j - k] + dp[i][k]) където k може да бъде в диапазона [1 j - 1].
Най-накрая минимумът от всички съкращения ще бъде отговорът. Но и това решение е неправилно.
Защо вертикалното или хоризонталното рязане с подхода за динамично програмиране няма да работи?
Това няма да работи, защото приемаме, че вертикален или хоризонтален разрез винаги ще разделя правоъгълника на две части. Помислете за хартия с размер 13x11 тогава, ако се опитаме да изрежем хартията, използвайки DP подход, ще получим 8 квадрата, но правилният отговор (както е показано в примерите) е 6. Следователно динамичното програмиране няма да работи.
[Правилен подход] Използване на DFS и динамично програмиране
C++The идея е да изрежете цялата хартия, като използвате DFS в отдолу нагоре начин. Във всяка стъпка намерете най-долния ляв ъгъл на хартията и се опитайте да изрежете квадрати с всички възможни размери от този ъгъл. След като изрежете квадрат отново, намерете най-долния ляв ъгъл на останалата хартия, за да изрежете квадрати с всички възможни размери и така нататък. Но ако опитаме всички възможни разфасовки от най-долния ляв ъгъл на всеки възможен размер хартия, тогава ще бъде доста неефективно. Можем да го оптимизираме, като използваме Динамично програмиране за съхраняване на минимални разфасовки за всеки възможен размер хартия.
За да идентифицираме уникално всеки размер хартия, можем да поддържаме масив remSq[], така че remSq[i] да съхранява броя на оставащите квадратчета с размер 1x1 в i-тата колона на хартията. Така че за хартия с размер 6x7 remSq[] = {6 6 6 6 6 6 6}. Също така, за да намерим най-долния ляв ъгъл, ще намерим първия индекс с максималния брой оставащи квадратчета. Така че можем да хешираме стойността на масива remSq[], за да намерим уникален ключ за всички възможни стойности на масива remSq[].
предаване на sql
// C++ Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb #include
// Java Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb import java.util.*; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int base = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Map<Integer Integer> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.containsKey(key)) return memo.get(key); int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = Arrays.copyOf(remSq b); int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo.put(key ans); return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; Arrays.fill(remSq a); Map<Integer Integer> memo = new HashMap<>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Sample Input int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb System.out.println(minCut(a b)); } }
# Python Program to find minimum number of squares to cut # from a paper of size axb # function to get the hash key for remSq array def getKey(remSq b): base = 1 key = 0 for i in range(b): key += remSq[i] * base base = base * (b + 1) return key # Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts # for a given remSq array def minCutUtil(remSq a b memo): # pointers to mark the start and end of range # with maximum remaining squares start = 0 # Check if we have previously calculated the answer # for the same state key = getKey(remSq b) if key in memo: return memo[key] maxRemSq = 0 # Find the starting point of min height for i in range(b): if remSq[i] > maxRemSq: maxRemSq = remSq[i] start = i # If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already # cut the entire paper if maxRemSq == 0: return 0 end = start newRemSq = remSq[:] ans = float('inf') # Find the ending point of min height while end < b: # length of edge of square from start till current end squareEdge = end - start + 1 # If the current column does not have maximum remaining # squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of # size squareEdge then break out of the loop if newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq or newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0: break # If we can cut a square of size squareEdge # update the remainingSquares for i in range(start end + 1): newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge # Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)) end += 1 memo[key] = ans return ans # Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut # using paper of size a X b def minCut(a b): # if the given rectangle is a square if a == b: return 1 # Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns remSq = [a] * b memo = {} return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) if __name__ == '__main__': # Sample Input a = 13 b = 11 # Function call to get minimum number # of squares for axb print(minCut(a b))
// C# Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb using System; using System.Collections.Generic; class GfG { // function to get the hash key for remSq array static int getKey(int[] remSq int b) { int baseVal = 1; int key = 0; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * baseVal); baseVal = baseVal * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array static int minCutUtil(int[] remSq int a int b Dictionary<int int> memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares int start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state int key = getKey(remSq b); if (memo.ContainsKey(key)) return memo[key]; int maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq == 0) return 0; end = start; int[] newRemSq = (int[])remSq.Clone(); int ans = int.MaxValue; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end int squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] != maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.Min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b static int minCut(int a int b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a == b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns int[] remSq = new int[b]; for (int i = 0; i < b; i++) remSq[i] = a; Dictionary<int int> memo = new Dictionary<int int>(); return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } static void Main() { int a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb Console.WriteLine(minCut(a b)); } }
// JavaScript Program to find minimum number of squares to cut // from a paper of size axb // function to get the hash key for remSq array function getKey(remSq b) { let base = 1; let key = 0; for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { key += (remSq[i] * base); base = base * (b + 1); } return key; } // Recursive function to find the minimum number of square cuts // for a given remSq array function minCutUtil(remSq a b memo) { // pointers to mark the start and end of range // with maximum remaining squares let start = 0 end; // Check if we have previously calculated the answer // for the same state let key = getKey(remSq b); if (key in memo) return memo[key]; let maxRemSq = 0; // Find the starting point of min height for (let i = 0; i < b; i++) { if (remSq[i] > maxRemSq) { maxRemSq = remSq[i]; start = i; } } // If max remaining squares = 0 then we have already // cut the entire paper if (maxRemSq === 0) return 0; end = start; let newRemSq = remSq.slice(); let ans = Infinity; // Find the ending point of min height while (end < b) { // length of edge of square from start till current end let squareEdge = end - start + 1; // If the current column does not have maximum remaining // squares or if it's impossible to cut a square of // size squareEdge then break out of the loop if (newRemSq[end] !== maxRemSq || newRemSq[end] - squareEdge < 0) break; // If we can cut a square of size squareEdge // update the remainingSquares for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) newRemSq[i] = maxRemSq - squareEdge; // Find the solution for new remainingSquares ans = Math.min(ans 1 + minCutUtil(newRemSq a b memo)); end += 1; } memo[key] = ans; return ans; } // Function to find the minimum number of squares we can cut // using paper of size a X b function minCut(a b) { // if the given rectangle is a square if (a === b) return 1; // Initialize remaining squares = a for all the b columns let remSq = new Array(b).fill(a); let memo = {}; return minCutUtil(remSq a b memo); } // Driver Code let a = 13 b = 11; // Function call to get minimum number // of squares for axb console.log(minCut(a b));
Изход
6
Времева сложност: O(a^b) за всяка от b колони можем да имаме квадратчета.
Помощно пространство: O(a^b) поради мемоизация, съхраняваща всяко уникално състояние.

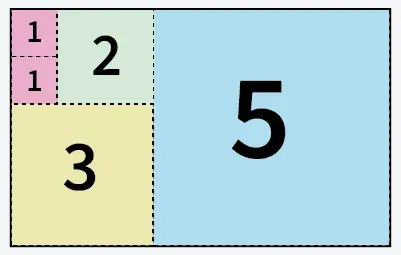 5 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 5 X 8
5 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 5 X 8 6 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 13 X 11
6 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 13 X 11 5 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 6 X 7
5 квадрата, изрязани от хартия с размер 6 X 7